selinux
카테고리: selinux
태그: selinux
SELlinux
- SELinux(Security-Enhanced Linux = 보안 강화 리눅스)
- 미국의 NSA(National Security Agency)에서 개발한 보안이 강화된 Linux Kernel Module
- 미국 국방부 스타일의 강제적 접근 제어(MAC)를 포함한 접근 제어 보안 정책을 지원하는 매커니즘을 제공하는 리눅스 커널 보안 모듈
- 사용자, 프로그램, 프로세스 그리고 이들의 동작 대상인 파일과 디바이스를 포함한 시스템 전체, 즉, 모든 주체와 객체에 대한 접근 허가(access permissions)를 기술
- SELinux는 매우 정밀한 상세 설정을 포함하여 어떠한 활동을 시스템이 개별 사용자, 프로세스, 데몬에 허용할 것인지를 잠재적으로 제어할 수 있음
-
시스템 또는 데몬(프로세스)가 버그(취약점)에 의해 공격 당하여 공격자에게 권한이 탈취당할 경우 해당 사용자의 권한이 미치는 모든 파일 들에 접근이 가능하여 위험해지게 됨
→ SELinux 적용
- SELinux 특징
-
기존 접근 통제 규칙보다 먼저 동작하므로 SELinux 의 보안 정책에 맞지 않을 경우 차단
-
보안의 기본 rule은 Deny All
-
서버 보안 상 상당히 유리하지만 적용이 단순하지 않고 복잡 함
SELinux가 시행(Enforcing) 상태 시 예외적인 규칙을 설정하지 않으면 모두 차단해 버리기 때문에 기존의 서비스 설정에도 서비스에 접근이 불가능한 상황 발생(대부분의 사용자들이 기능을 종료하는 방법으로 해결)
특정 서비스가 SELinux에 의해 동작하지 않을 경우 SELinux를 종료하기 보다 서비스에 대한 SELinux 설정을 수정하여 서비스를 구동시키는 것을 권장
-
SELinux가 실행되면 리눅스 user 및 SELinux user가 각각 존재하며 리눅스 user는 SELinux user에 매핑됨
-
활성화 되는 프로세스를 Subject(주체)라고 하며, 주체를 통해 액세스되는 파일, 소켓, 파이프 또는 네트워크 인터페이스와 같은 리소스를 Object(객체) 라고 함
-
-
설정파일
[root@localhost 바탕화면]# vi /etc/sysconfig/selinux
-
활성화 하기
-
설정 파일 수정

-
재시작 후 확인
[root@localhost 바탕화면]# reboot [root@localhost 바탕화면]# sestatus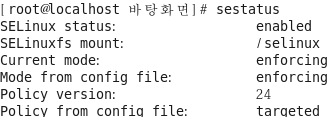
[root@localhost 바탕화면]# getenforce
-
재시작 안하고 임시로 변경
임시로 변경은 가능하나 재시작후 기본값으로 돌아온다
[root@localhost 바탕화면]# setenforce -h
[root@localhost 바탕화면]# setenforce 0 [root@localhost 바탕화면]# getenforce
[root@localhost 바탕화면]# setenforce 1 [root@localhost 바탕화면]# getenforce
-
-
관련 패키지 설치
-
SELinux(setools-console Package)
SELinux 정책을 분석 및 질의, 감사 로그 모니터링 보고, 파일 컨텍스트 관리를 위한 여러 도구 및 라이브 러리를 제공
seaudit-report, sechecker, sediff, seinfo, sesearch 등의 도구 포함
# yum install setools-console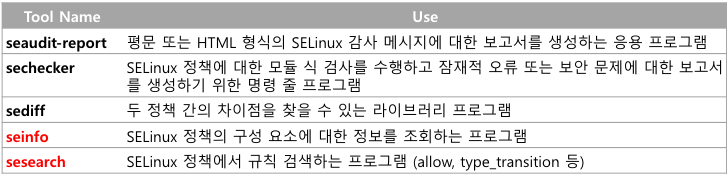
-
semanage
SELinux 의 보안 정책을 조회하고 추가/변경/삭제할 수 있는 명령행 기반의 유틸리티
policycoreutils-python 패키지 설치 후 사용
# yum install policycoreutils-python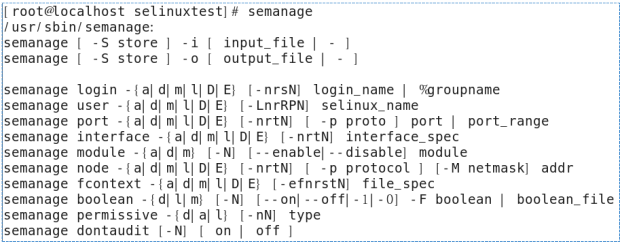
-
SELinux Security Context
SELinux 는 모든 프로세스와 객체 마다 보안 컨텍스트(= 보안 레이블 = 보안 태그) 정보를 부여하여 관리
접근 권한을 확인하는데 사용됨
-
-
주체에 대한 컨텍스트
-
주체 : 파일 ,프로세스 …
-
파일에 대한 보안태(보안컨텍스트) 확인
[root@localhost ~]# mkdir /root/selinuxtest [root@localhost ~]# cd /root/selinuxtest/ [root@localhost selinuxtest]# touch testfile [root@localhost selinuxtest]# ls -R /root/selinuxtest/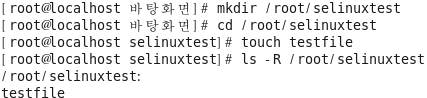
[root@localhost selinuxtest]# mkdir /root/selinuxtest/testdir [root@localhost selinuxtest]# ls -Z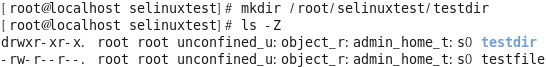
-
프로세스에 대한 보안태그(보안컨텍스트) 확인
# rpm -qa | grep httpd
[root@localhost selinuxtest]# ps -ZC httpd
보이지 않으면 서비스/데몬 재시작후 확
[root@localhost selinuxtest]# service httpd restart [root@localhost selinuxtest]# ps -ZC httpd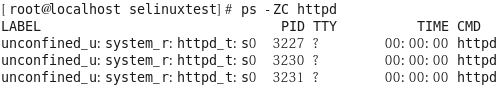
-
-
Security Context 형식

-
사용자(user)
SELinux 사용자 ID
시스템의 사용자와는 별도의 SELinux 사용자이며 역할이나 레벨과 연계하여 접근 권한을 관리하는데 사용됨
SELinux 사용자가 사용할 수 있는 하나 이상의 역할과 연관 될 수 있음
SELinux 사용자에게 제약 조건과 경계를 추가 할 수 있음
일반적으로 마지막에 ‘_u’로 표시 됨
SELinux 정책을 통해 SELinux 사용자에 매핑 됨
[root@localhost selinuxtest]# seinfo -u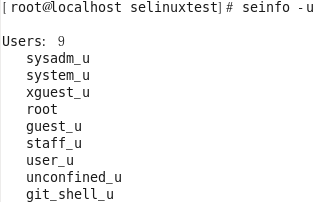
시스템 계정과 SELinux 사용자가 어떻게 연결되어 있는지 조회 [root@localhost selinuxtest]# semanage login -l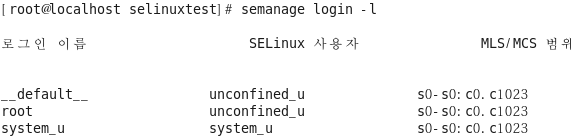
-
역할(Role)
객체와 주체의 역할을 지정
TE(Type Enforcement) 도메인에 대한 액세스를 추가로 제어하기 위해 SELinux는 역할 기반 액세스 제어 (RBAC)를 사용
SELinux 사용자가 액세스 할 수 있는 하나 이상의 유형과 연관 될 수 있음
사용자 역할이 접근할 수 있는 영역들은 정책 설정 파일에 의해서 미리 정의되어 있음
일반적으로 마지막에 ‘_r’로 표시 됨
[root@localhost selinuxtest]# seinfo -r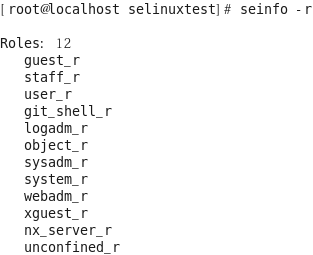
각 SELINUX user 에 연결된 role [root@localhost selinuxtest]# seinfo -uunconfined_u -x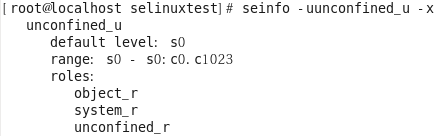
-
유형(Type or Domain)
TE(Type Enforcement)의 속성 중 하나로 프로세스의 도메인이나 파일의 타입을 지정하고 이를 기반 으로 접근 통제를 수행
실제 접근 권한이 결정되는 항목
영역(domain) → 프로세스 등의 주체에 적용
> 모든 프로세스는 영역 내에서 동작하게 되며, 영역은 프로세스에게 어떠한 접근을 가질 것인가를 결정
유형(type) → 디렉토리, 파일, 소켓 등의 객체에 적용
> 그 객체에 어떤 주체가 접근할 수 있는지를 결정
영역과 유형의 보안 속성은 일반적으로 마지막 ‘_t’로 표시 됨
타입과 도메인의 목록 확인 [root@localhost selinuxtest]# seinfo -t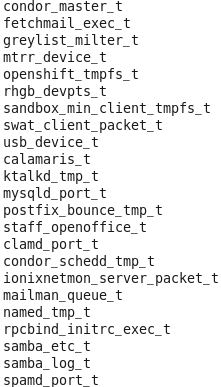
-
-
파일 제어
-
웹서버 동작 여부 확인

-
웹서버에 파일 추가후 다시 확인
# echo "SELinux TEST" > /var/www/html/setest.html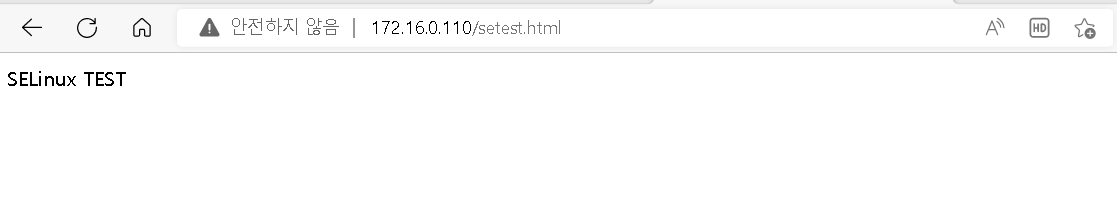
-
새로 추가된 파일에 대한 보안 컨텍스트를 확인
[root@localhost selinuxtest]# ls -Z /var/www/html/setest.html
상위 디렉터리에서 상속 [root@localhost selinuxtest]# ls -Z /var/www/html
-
주체가 객체에 어떻게 접근하고 있는지 확인
프로세스의 정책 확인 [root@localhost selinuxtest]# ps -ZC httpd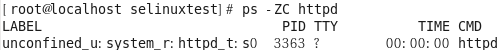
프로세스가 파일에 어떤 허용정책 있는지 확인 [root@localhost selinuxtest]# sesearch -A -t httpd_sys_content_t -s httpd_t -d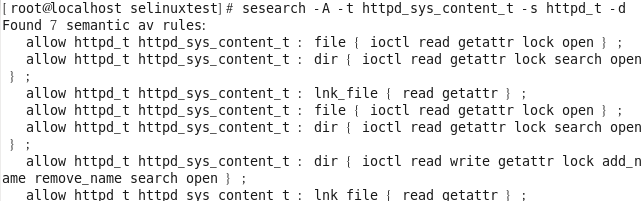
-
기존 정책 대신 비어있는 정책 포함
/var/www/html/setest.html 에 적용된 httpd_sys_content_t 를 삭제 -> 다른 비어있는 정책과 연결 [root@localhost selinuxtest]# chcon -t admin_home_t /var/www/html/setest.html [root@localhost selinuxtest]# ls -Z /var/www/html/setest.html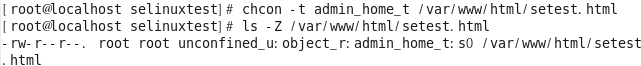
연결된 정책에 항목이 없음 (비어있음) [root@localhost selinuxtest]# sesearch -A -t admin_home_t -s httpd_t -d
다시 브라우저로 테스트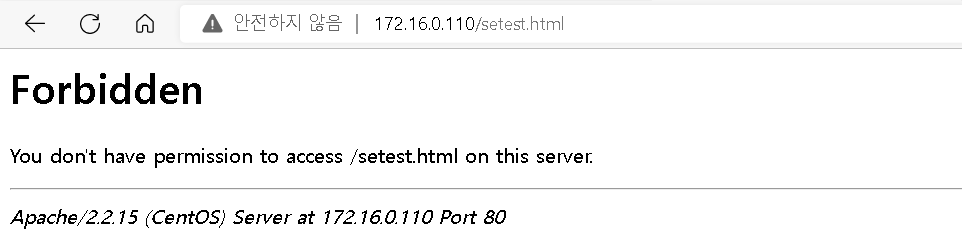
-
원상복구
복구시에 이렇게 복구된다 [root@localhost selinuxtest]# matchpathcon /var/www/html/setest.html
실제 보안 컨텍스트 복구 시도 [root@localhost selinuxtest]# restorecon /var/www/html/setest.html [root@localhost selinuxtest]# ls -Z /var/www/html/setest.html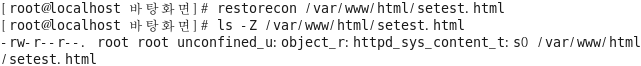
-
-
포트 제어
-
httpd 기본포트
[root@localhost selinuxtest]# netstat -antup | grep httpd
[root@localhost selinuxtest]# grep Listen /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
-
포트번호 TCP 8888 로 변경하여 서비스 테스트
# vim /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
# service httpd restart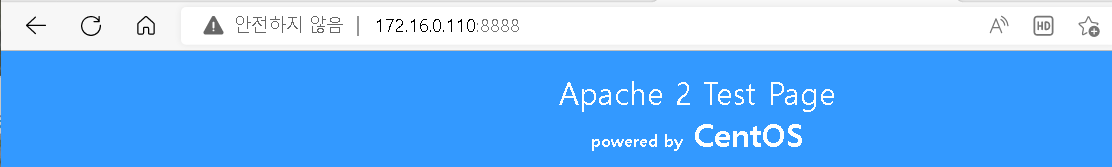
SELINUX 원상복원 : bool 값을 수정 [root@localhost selinuxtest]# setenforce 1 [root@localhost selinuxtest]# getenforce
-
특정 포트에 대한 정책 확인
TCP 80 [root@localhost selinuxtest]# seinfo --portcon=80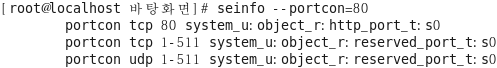
-
특정 타입에서 사용 가능한 포트 번호 확인
[root@localhost selinuxtest]# semanage port -l | grep http_port_t
-
사용가능한 다른포트 확인
tcp 9000 테스트 # vim /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
[root@localhost selinuxtest]# service httpd restart
-
특정한 프로토콜이 사용하는 정책 및 포트 번호 확인
[root@localhost selinuxtest]# semanage port -l | grep http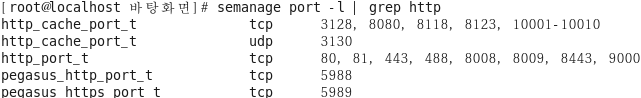
[root@localhost selinuxtest]# semanage port -l | grep ssh
[root@localhost selinuxtest]# semanage port -l | grep ftp
-
객체: 포트(=socket) 에 대한 주체(프로세스)의 접근 정책
[root@localhost selinuxtest]# sesearch -A -t http_port_t -s httpd_t -d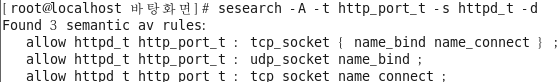
[root@localhost selinuxtest]# sesearch -A -t http_cache_port_t -s httpd_t -d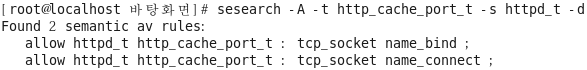
이름이 없음 [root@localhost selinuxtest]# sesearch -A -t pegasus_http__port_t -s httpd_t -d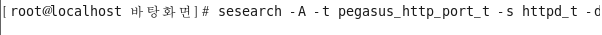
연결된 포트 X [root@localhost selinuxtest]# sesearch -A -t pegasus_http_port_t -s httpd_t -d [root@localhost selinuxtest]# sesearch -A -t pegasus_https_port_t -s httpd_t -d -
포트 추가후 서비스 확인
TCP 8888 변경하여 서비스 재시작 오류 확인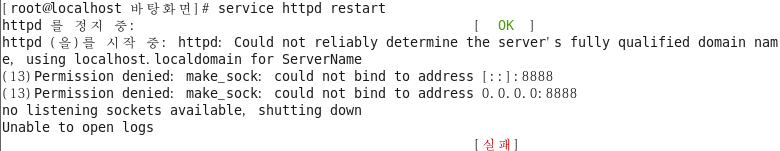
http_port_t 에 허용 포트 추가 [root@localhost selinuxtest]# semanage port -a -t http_port_t -p tcp 8888 추가 확인 [root@localhost selinuxtest]# semanage port -l | grep http_port_t
[root@localhost selinuxtest]# service httpd restart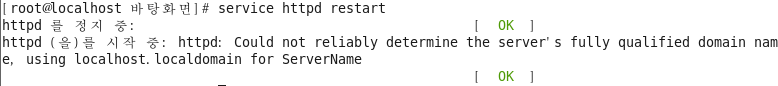
-
SELinux Logging
- SELinux Log
-
기본 로그 저장 파일 : /var/log/audit/audit.log
-
vim /var/log/audit/audit.log
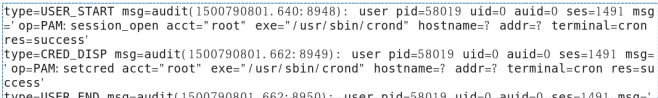
-
로그 관리를 위한 추가 유틸리티
audit2why
ausearch
setroubleshoot-server 패키지(sealert)
[root@localhost selinuxtest]# cd /var/log/audit/ [root@localhost audit]# vim ./audit.log -
로그관리 패키지 설치 후 서비스 시작
setroubleshoot-server 패키지
> python 으로 만들어진 유틸리티로 어려운 SELinux AVC 메시지를 알기 쉽게 번역해 주고 처리 방안도 제시해 주는 유틸리티
> messagebus 데몬 필요(기본 데몬으로 패키지 설치 후 재 시작만 해주면 됨)
[root@localhost audit]# yum -y install setroubleshoot-server [root@localhost audit]# service messagebus restart -
테스트를 위한 에러 발생을 유도
터미널1) # tail -f /var/log/audit/audit.log터미널2) /var/www/html/setest.html 에 적용된 httpd_sys_content_t 를 삭제 -> 다른 비어있는 정책과 연결 [root@localhost selinuxtest]# chcon -t admin_home_t /var/www/html/setest.html [root@localhost selinuxtest]# ls -Z /var/www/html/setest.html
웹서버 포트 번호 터미널1) 로그 기록 확인 > 아직 보이는 것 이 없음 host) http://웹서버:8888/setest.html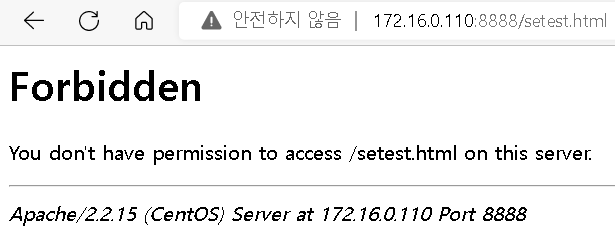
터미널 1)
터미널 2) # cat /var/log/messages
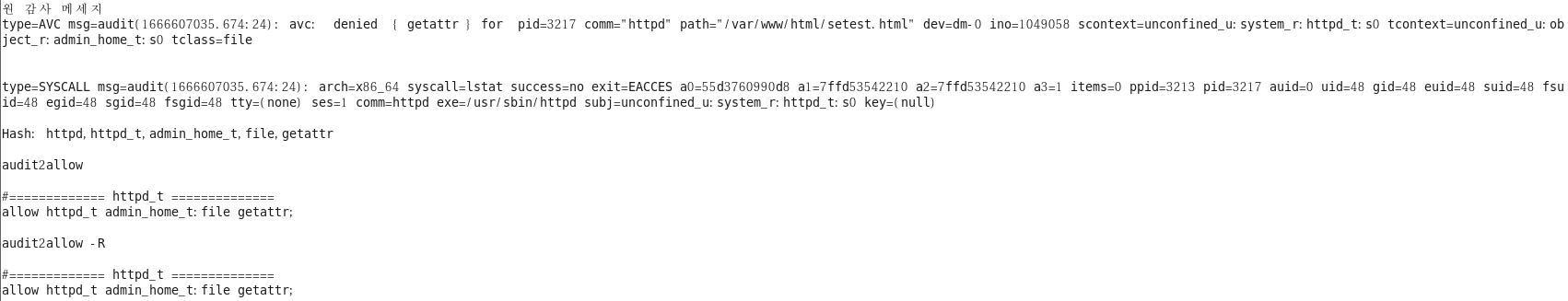
[root@localhost ~]# sealert -l 1fc23662-db19-403d-9fe7-63868d4e1d42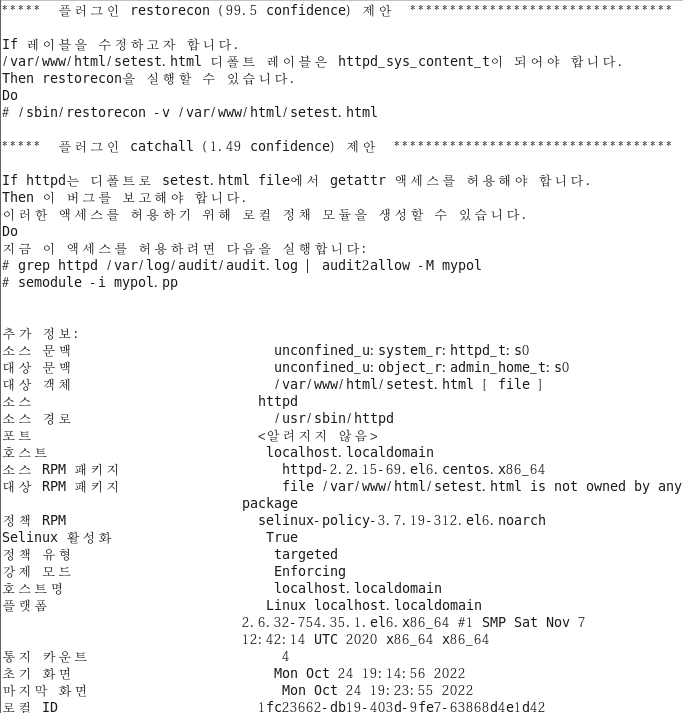
-
SELNUX Boolean
- SELinux Boolean
-
SELinux가 적용될 경우 특정 데몬의 서비스가 SELinux에 의해서 거부되며, 설정을 변경하지 않으면 해당 서비스 이용에 상당한 제약을 받게 됨
-
SELinux 정책 작성에 대한 지식 없이 런타임에 SELinux 정책의 일부를 변경할 수 있게 함
-
이 경우 정책을 다시 로드하거나 다시 컴파일하지 않고도 서비스 액세스 허용 등의 변경 작업 수행
-
Bool 값 확인
[root@localhost ~]# getsebool -a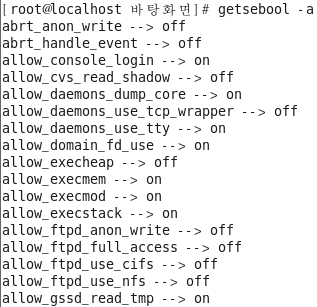
-
기능 설명
[root@localhost ~]# semanage boolean -l
-
특정 정책 조회
[root@localhost ~]# getsebool httpd_can_sendmail
-
조회된 정책을 켜고 싶으면 on , 1, true
[root@localhost ~]# setsebool httpd_can_sendmail true [root@localhost ~]# getsebool httpd_can_sendmail
-
조회된 정책을 끄고 싶으면 off, 0 , false
[root@localhost ~]# setsebool httpd_can_sendmail false [root@localhost ~]# getsebool httpd_can_sendmail
영구 적용 하는 경우 -P 옵션 사용할것
-
-
httpd 프로세스가 php 페이지 이용 메일 보내기
-
php 설치
yum -y install httpd php -
리눅스내 다른 계정으로 매일 보내기 연습
httpd , php 설치 여부를 확인 [root@localhost ~]# rpm -qa httpd [root@localhost ~]# rpm -qa php
-
테스트 파일을 생성
# vim /var/www/html/mail.php
-
정책확인 후 다시 적용
[root@localhost ~]# setsebool httpd_can_sendmail 1 [root@localhost ~]# getsebool httpd_can_sendmail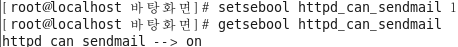
-
다시 원상복구
[root@localhost ~]# setsebool httpd_can_sendmail 0 [root@localhost ~]# getsebool httpd_can_sendmail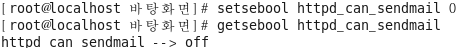
-
해당 페이지를 열어서 관련 로그 확인
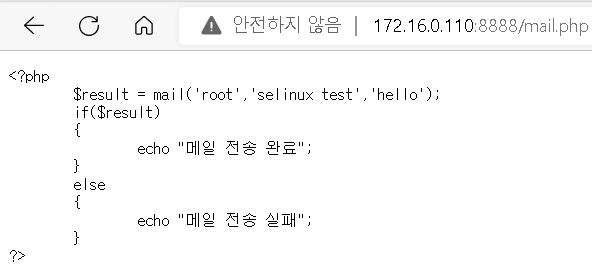
-
httpd 를 다시 실행하여 php 사용
[root@localhost ~]# service httpd restart -
다시 페이지에 접속시도

-
다시 로그 확인
[root@localhost ~]# tail /var/log/messages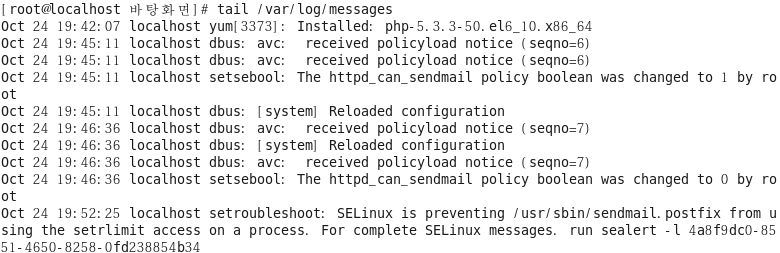
-
자세한 SELINUX 정보 확인
[root@localhost ~]# sealert -l 4a8f9dc0-8551-4650-8258-0fd238854b34
-
다시 SELNUX bool 수정후 확인
[root@localhost 바탕화면]# setsebool -P httpd_can_sendmail=1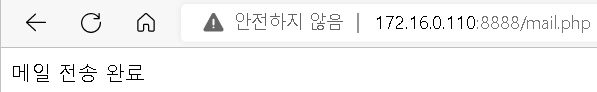
-
메시지 확인
[root@localhost ~]# cat /var/spool/mail/root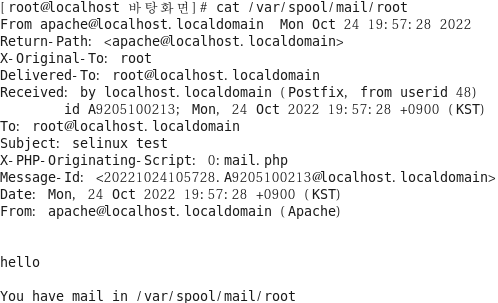
-
-
ftp 접속제한

-
vsftpd 설치후 시작
# yum -y install vsftpd # service vsftpd restart -
host] 알드라이브로 일반 사용자 접속 확인
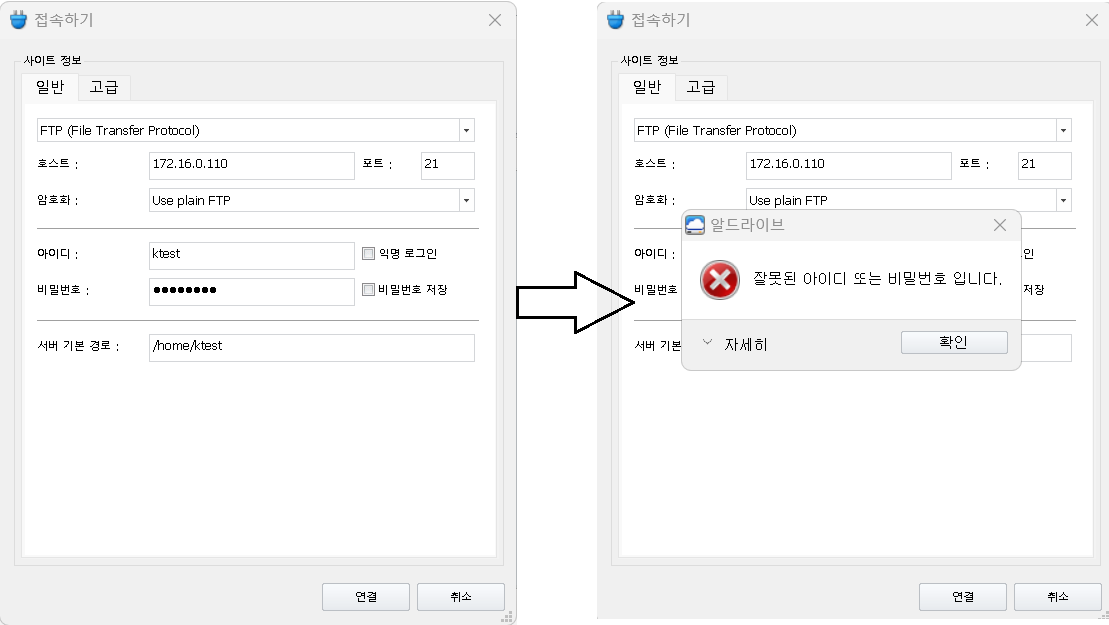
-
접속 가능하도록 설정
[root@localhost ~]# setsebool ftp_home_dir true [root@localhost ~]# getsebool ftp_home_dir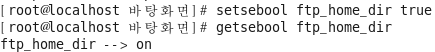
-
다시 접속 시도
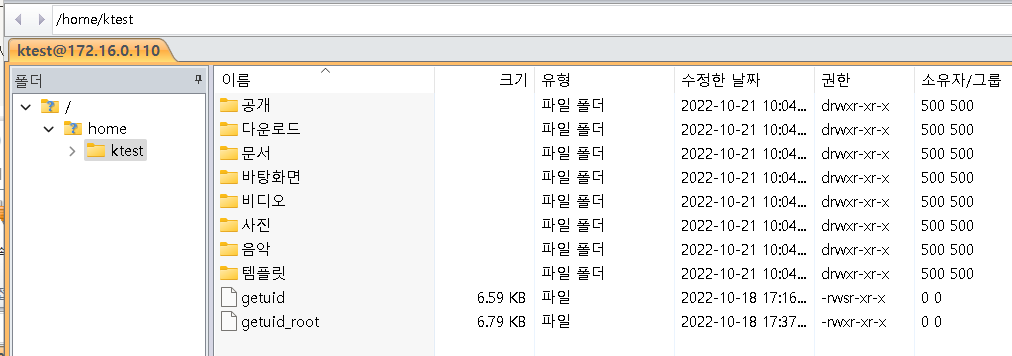
-

댓글 남기기